
Build and push docker images to ACR using Azure DevOps pipelines
Build and push docker images to Azure Container Registry using Azure DevOps pipelines In this blog, I’ll show you how to create azure container …
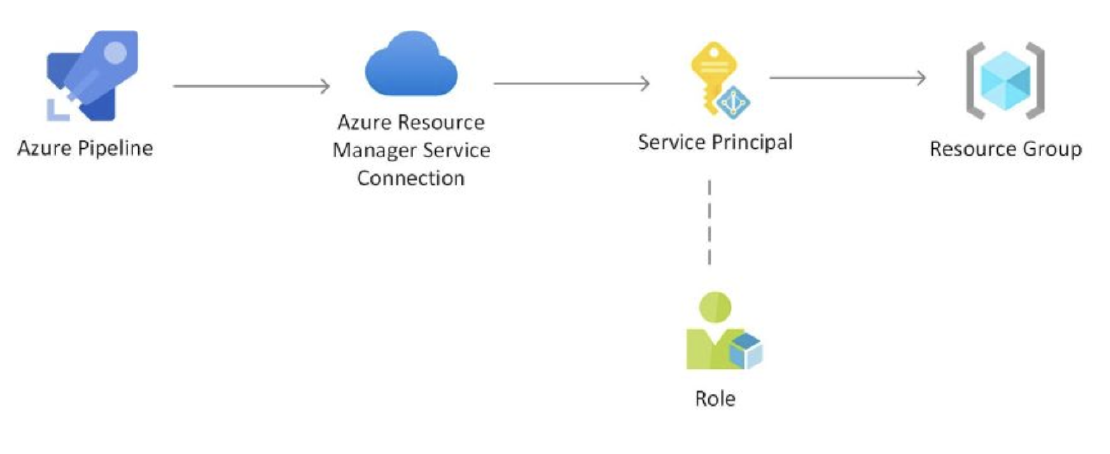
Azure DevOps and Azure Pipeline are powerful tools for automating the deployment of infrastructure as code. By combining these tools with Terraform, we can deploy Azure resources quickly and efficiently. In this article, we will walk through the steps required to set up Azure DevOps and Azure Pipeline to deploy Azure resources via Terraform.
The first step is to create a service connection in the Azure DevOps project. This connection will allow the pipeline to communicate with Azure and deploy resources.
To create a service connection, follow these steps:
Project Settings → Service connectionsNew service connectionAzure Resource ManagerOnce the connection is created, we can move on to creating a variable group. This group will store key-value pairs that can be referenced in the pipeline’s YAML file.
To create a variable group, follow these steps:
Pipelines → Library → Variable groupNew variable groupdev) and add key-value pairsgroup: dev and $(SUBSCRIPTION_ID)Finally, we need to add the Terraform tasks to the YAML file. This will allow the pipeline to run Terraform commands and deploy resources.
To add Terraform tasks, follow these steps:
Here’s an example of what the YAML file might look like:
variables:
- group: dev
- name: armServiceConnection
value: 'ARM_SERVICE_CONNECTION'
- task: AzureCLI@2
displayName: 'Deploy Web App'
inputs:
azureSubscription: ${{ variables.armServiceConnection }}
scriptType: bash
scriptLocation: inlineScript
addSpnToEnvironment: true
inlineScript: |
make deploy \
ARM_CLIENT_ID=$servicePrincipalId \
ARM_CLIENT_SECRET=$servicePrincipalKey \
ARM_SUBSCRIPTION_ID=$(SUBSCRIPTION_ID) \
ARM_TENANT_ID=$tenantId \
TF_VAR_identifier='$(Build.sourceBranchName)'
In this example, the AzureCLI task is used to log in to Azure and set the subscription. The env section contains environment variables that Terraform will use to deploy resources.
azureSubscription refers to the service connection name that was created earlier.
ARM_SUBSCRIPTION_ID is the subscription ID that is stored in the service connection.
ARM_CLIENT_ID, ARM_CLIENT_SECRET, and ARM_TENANT_ID are other required parameters that are automatically populated once the service connection is created.
addSpnToEnvironment needs to be set to true to allow using the service principle for login instead of personal credentials. By default, it is set to false.
Other Terraform environment variables can be set using the TF_VAR_ prefix.

Build and push docker images to Azure Container Registry using Azure DevOps pipelines In this blog, I’ll show you how to create azure container …

How to Assign a Custom Role to a Service Principal in Azure DevOps Azure DevOps provides a seamless integration with Azure Active Directory (AAD) for …